Celiac.com 04/20/2010 - A team of researchers recently set out to determine whether new serology assays can detect gluten sensitivity among enteropathy patients seronegative for anti–tissue transglutaminase.
Emilia Sugai, Hui Jer Hwang, Horacio Vázquez, Edgardo Smecuol, Sonia Niveloni, Roberto Mazure, Eduardo Mauriño, Pascale Aeschlimann, Walter Binder, Daniel Aeschlimann and Julio C. Bai comprised the research team.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
They are variously affiliated with the Small Bowel Section of the Department of Medicine at C. Bonorino Udaondo Gastroenterology Hospital in Buenos Aires, Argentina, the Matrix Biology and Tissue Repair Research Unit at the Cardiff University School of Dentistry in Cardiff, UK, and with INOVA Diagnostics, Inc., of San Diego, California.
Some patients with celiac disease may not show a normal positive reaction to the test most commonly used for IgA anti–tissue transglutaminase (anti-tTG) antibodies.
The research team set out to determine the usefulness of newer assays incorporating synthetic deamidated gliadin-related peptides (DGPs), or other TG isoenzymes as antigen, for detecting gluten sensitivity in IgA anti-tTG–seronegative patients.
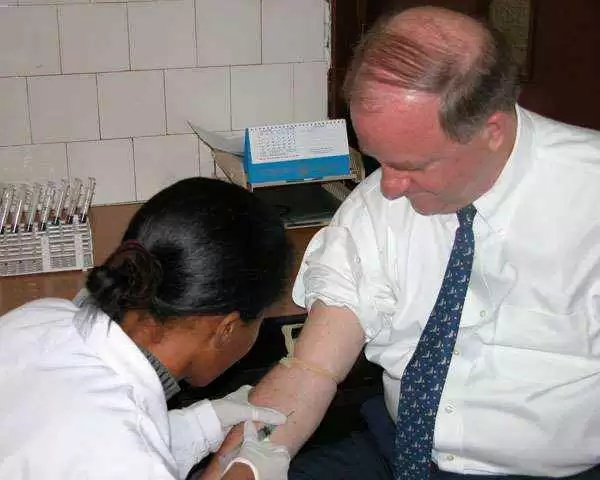
The team tested blood samples drawn at diagnosis from 12 anti-tTG–seronegative patients with a celiac-like enteropathy, from 26 patients with skin biopsy–proven dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) and, lastly, from 26 patients with IgA anti-tTG–positive celiac disease.
All patients showed typical levels of total IgA. On each patient, the team conducted intestinal biopsy and serum testing for detection of IgA and IgG isotypes of both anti-DGP and anti-tTG in a single assay (tTG/DGP Screen; INOVA Diagnostics). They also tested each patient for simultaneous detection of both IgA and IgG anti-DGP antibody isotypes (DGP Dual; INOVA Diagnostics). Lastly, they tested each patient for the detection of antibodies to transglutaminase 3 (TG3) or transglutaminase 6 (TG6).
All patients who showed positive anti-tTG results also tested positive in anti-DGP assays.
The tTG/DGP Screen caught six of the 19 anti-tTG seronegatives (31.6%), while anti-DGP Dual produced caught five of these cases (26.3%). Whereas both assays detected 2 anti-tTG–negative DH patients with partial villous atrophy, they were positive in only 2 of the 5 cases with no histologically discernible mucosal damage. Testing for antibodies to TG3 and TG6 caught seven of the 19 anti-tTG–negative patients (36.8%), five of whom also tested positive for anti-DGP.
From these results, the team concludes that using tTG/DGP Screen, or anti-DGP Dual, to detect anti-DGP improves diagnostic sensitivity of gluten sensitive patients with non–IgA- deficiency, or anti-tTG–seronegativity, and celiac-like enteropathy. The same enhancement is also achieved by detecting antibodies to other TG isoenzymes.
Source:
- Open Original Shared Link




Recommended Comments