Celiac.com 03/21/2018 - Many people with celiac disease suffer from non-gastrointestinal symptoms. Here are 15 non-gastrointestinal symptoms that can make celiac disease difficult to diagnose. If the general public knows anything about celiac disease, it is likely that eating wheat can cause stomach problems in people with the condition. And that’s often true, classical celiac symptoms include abdominal bloating and pain, chronic diarrhea and/or constipation, and vomiting.
Young children are more likely to show classic signs of celiac disease, including growth problems (failure to thrive, chronic diarrhea/constipation, recurring abdominal bloating and pain, fatigue, and irritability.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
Older children and adults tend to have symptoms that are not entirely gastrointestinal in nature.
So, depending on age, and other factors, celiac disease affects different people differently. In fact, there are more than 200 signs and symptoms of celiac disease. Some patients have several, some just a few. Many report non-gastrointestinal symptoms. And many people with celiac disease never show any symptoms at all.
Yet, both people with vague symptoms and those with no symptoms still face a higher risk of developing complications associated with celiac disease, as well as for celiac-associated conditions.
Recent research has demonstrated that only a third of adult patients diagnosed with celiac disease experience diarrhea. Weight loss is also not a common sign. In fact, far more patients diagnosed these days are over weight.
We’ve covered the most common physical complaints of people with celiac disease, but here is a list of fifteen common non-gastrointestinal symptoms that can make celiac disease hard to diagnose:
1) ANEMIA—The most common non-gastrointestinal problem faced by people with celiac disease is anemia. About one in three celiacs (34%) suffer from anemia.
- Anemia and Celiac Disease
- Is Celiac Disease Worse In People With Anemia?
- Celiac Disease and Iron Deficiency Linked in Caucasians, But Not Non-Caucasians
2) BLOATING—20% of celiacs complained of bloating prior to diagnosis.
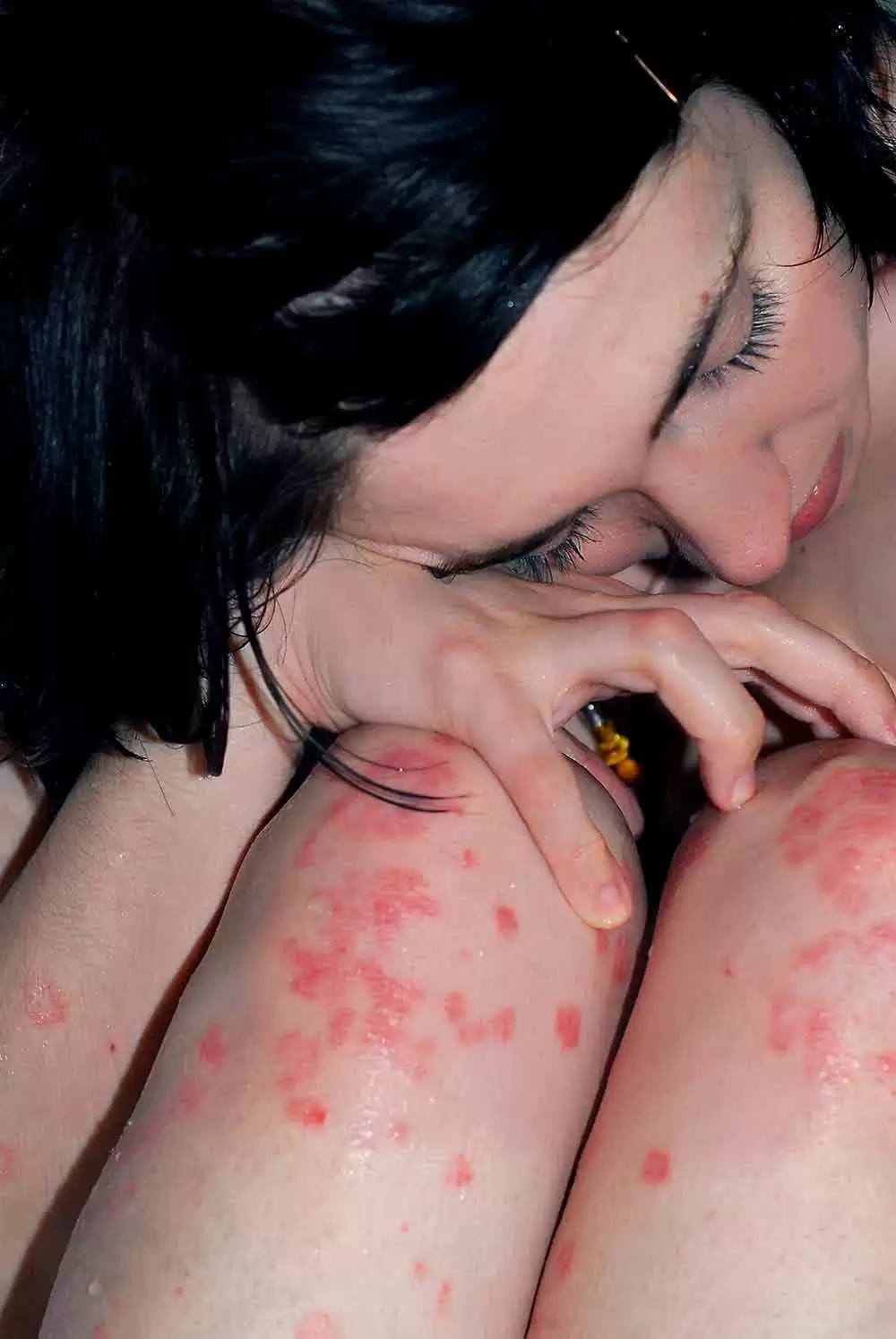
3) DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS, PSORIASIS & other skin conditions—Many people with celiac disease suffer from dermatitis herpetiformis, psoriasis, or other skin conditions.
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Skin Condition Associated with Celiac Disease
- Skin Problems and Celiac Disease
- Five Common Skin Conditions Associated With Celiac Disease
- Psoriasis and Celiac Disease
4) ATAXIA, NERVE DISEASE, NEUROPATHY—Many people with celiac disease suffer from ataxia, nerve disease, or neuropathy, especially peripheral neuropathy.
5) CRYPTOGENIC HYPERTRANSAMINASEMIA—nearly one-third (29%) of people with celiac disease, have what is called cryptogenic hypertransaminasemia, also known as celiac hepatitis.
6) THYROID DISEASE—Thyroid disorders are common in people with celiac disease.
- Thyroid & Pancreatic Disorders and Celiac Disease
- Should Patients with Autoimmune Thyroid Disease Be Screened for Celiac Disease?
7) JOINT PAIN—Joint pain is a common complaint of many people with celiac disease, possibly due to associated inflammation.
8) DENTAL ENAMEL DEFECTS—Researchers have recently linked dental enamel defects with celiac disease. In the future, dentists may play an important role in helping to diagnose celiac disease, especially in patients with non-classical or vague symptoms, by noting dental enamel defects common in people with celiac disease.
- Dental Enamel Defects Indicate Adult Celiac Disease
- Distinct Tooth Enamel Defects Can Help Reveal Celiac Disease
9) UNEXPLAINED INFERTILITY, RECURRENT MISCARRIAGE—Women who suffer from unexplained infertility an/or recurrent miscarriage have a much higher risk of celiac disease.
10) OSTEOPENIA/OSTEOPOROSIS—A full 52% of patients with celiac disease suffer from osteopenia/osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a more serious bone density problem. Many people with celiac disease suffer from low bone density.
11) PSORIASIS—Many people with celiac disease also have psoriasis. It’s also true that many people with psoriasis claim to find that a gluten-free diet can help their symptoms to improve.
12) PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS—Many people with celiac disease suffer from psychiatric disorders such as anxiety and depression. In some cases, especially in those without classic symptoms, these psychiatric disorders can be among the few symptoms, and can make celiac disease difficult to diagnose.
13) CANKER SORES (Aphthous Stomatitis)—People with celiac disease have much higher rates of canker sores. In fact, nearly 20% of people with symptomatic celiac disease had canker sores as one of their symptoms. In many cases, these canker sores are recurrent, and can be one of the few or only signs of celiac disease.
14) FATIGUE—Many people with celiac disease report recurrent fatigue as one of their symptoms. Sometimes, fatigue can be one of the few or only symptoms, making celiac disease difficult to diagnose.
15) WEIGHT GAIN—Classic celiac disease patients commonly suffered weight loss or low body weight. That has changed. These days, it is much more common for people with celiac disease to be overweight.
- Screening Versus Symptoms: Does Detection Method Affect Body Mass For Celiacs on a Gluten-Free Diet?
- How can I be overweight with Celiac ?
Sources:








Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now