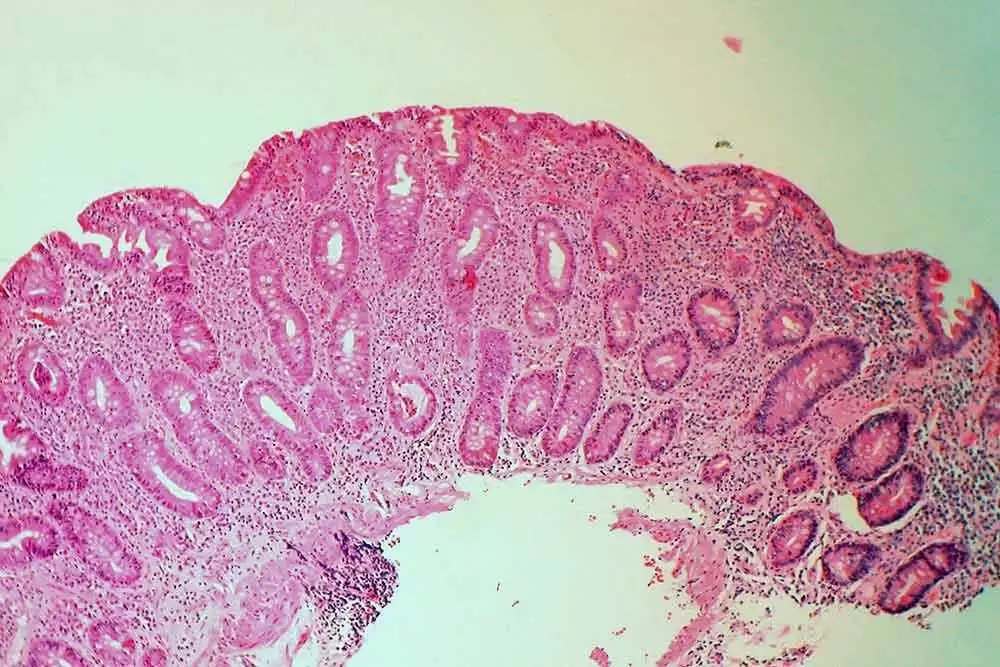
Celiac.com 06/13/2018 - There have been numerous reports that olmesartan, aka Benicar, seems to trigger sprue‐like enteropathy in many patients, but so far, studies have produced mixed results, and there really hasn’t been a rigorous study of the issue. A team of researchers recently set out to assess whether olmesartan is associated with a higher rate of enteropathy compared with other angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
The research team included Y.‐H. Dong; Y. Jin; TN Tsacogianis; M He; PH Hsieh; and JJ Gagne. They are variously affiliated with the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, MA, USA; the Faculty of Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Science at National Yang‐Ming University in Taipei, Taiwan; and the Department of Hepato‐Gastroenterology, Chi Mei Medical Center in Tainan, Taiwan.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
To get solid data on the issue, the team conducted a cohort study among ARB initiators in 5 US claims databases covering numerous health insurers. They used Cox regression models to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for enteropathy‐related outcomes, including celiac disease, malabsorption, concomitant diagnoses of diarrhea and weight loss, and non‐infectious enteropathy. In all, they found nearly two million eligible patients.
They then assessed those patients and compared the results for olmesartan initiators to initiators of other ARBs after propensity score (PS) matching. They found unadjusted incidence rates of 0.82, 1.41, 1.66 and 29.20 per 1,000 person‐years for celiac disease, malabsorption, concomitant diagnoses of diarrhea and weight loss, and non‐infectious enteropathy respectively.
After PS matching comparing olmesartan to other ARBs, hazard ratios were 1.21 (95% CI, 1.05‐1.40), 1.00 (95% CI, 0.88‐1.13), 1.22 (95% CI, 1.10‐1.36) and 1.04 (95% CI, 1.01‐1.07) for each outcome. Patients aged 65 years and older showed greater hazard ratios for celiac disease, as did patients receiving treatment for more than 1 year, and patients receiving higher cumulative olmesartan doses.
This is the first comprehensive multi‐database study to document a higher rate of enteropathy in olmesartan initiators as compared to initiators of other ARBs, though absolute rates were low for both groups.
Source:








Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now