
Celiac.com 04/20/2016 - People with celiac disease very often have reflux symptoms. A team of researchers recently set out to evaluate mucosal integrity and motility of the lower esophagus as possible contributors to reflux symptoms in patients with celiac disease.
The research team included María Inés Pinto-Sánchez, Fabio D. Nachman, Claudia Fuxman, Guido Iantorno, Hui Jer Hwang, Andrés Ditaranto, Florencia Costa, Gabriela Longarini, Xuan Yu Wang, Xianxi Huang, Horacio Vázquez, María L. Moreno, Sonia Niveloni, Premysl Bercik, Edgardo Smecuol, Roberto Mazure, Claudio Bilder, Eduardo C. Mauriño, Elena F. Verdu, and Julio C. Bai.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
They are variously affiliated with the Farncombe Family Digestive Health Research Institute at McMaster University, in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, the Department of Medicine, "Dr. Carlos Bonorino Udaondo" Gastroenterology Hospital in Buenos Aires, Argentina, Favaloro University Hospital in Buenos Aires, Argentina, Consejo de Investigación en Salud, MSAL, Gobierno de la Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, Argentina, and with the Gastroenterology Chair, Universidad del Salvador in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
For their study, they enrolled newly diagnosed celiac disease patients with and without reflux symptoms, non-celiac patients with classical reflux disease (GERD), and control subjects, who had no reflux symptoms.
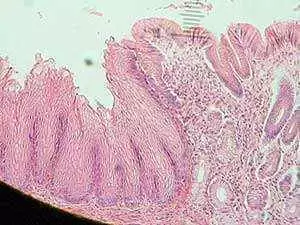
Using both light microscopy and electron microscopy, they assessed endoscopic biopsies from the distal esophagus for dilated intercellular space (DIS). They used qRT-PC to determine tight junction (TJ) mRNA proteins expression for zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and claudin-2 and claudin-3 (CLDN-2; CLDN-3).
Overall, patients with active celiac disease showed higher DIS scores than controls, and similar to GERD patients. They found altered DIS even in celiac disease patients without reflux symptoms, who had normalized after one year of a gluten-free diet.
Celiac disease patients with and without reflux symptoms had lower expression of ZO-1 than controls. Celiac disease and GERD patients showed similar expression of CLDN-2 and CLDN-3.
This study shows that patients with active celiac disease have altered esophageal mucosal integrity, independent of any reflux symptoms.
Loss of TJ integrity in the esophageal mucosa may result from altered expression of ZO-1, which may contribute to the development of reflux symptoms.
Source:
- Open Original Shared Link






Recommended Comments