Celiac.com 04/29/2024 - Tooth enamel, the protective layer covering our teeth, is vital for maintaining oral health. However, in some individuals, including those with celiac disease, flaws in enamel development can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and decay. Recent research from Prof. Jakub Abramson's team at the Weizmann Institute of Science has uncovered a new autoimmune disorder linked to defective enamel formation, shedding light on potential preventive measures.
The Importance of Tooth Enamel
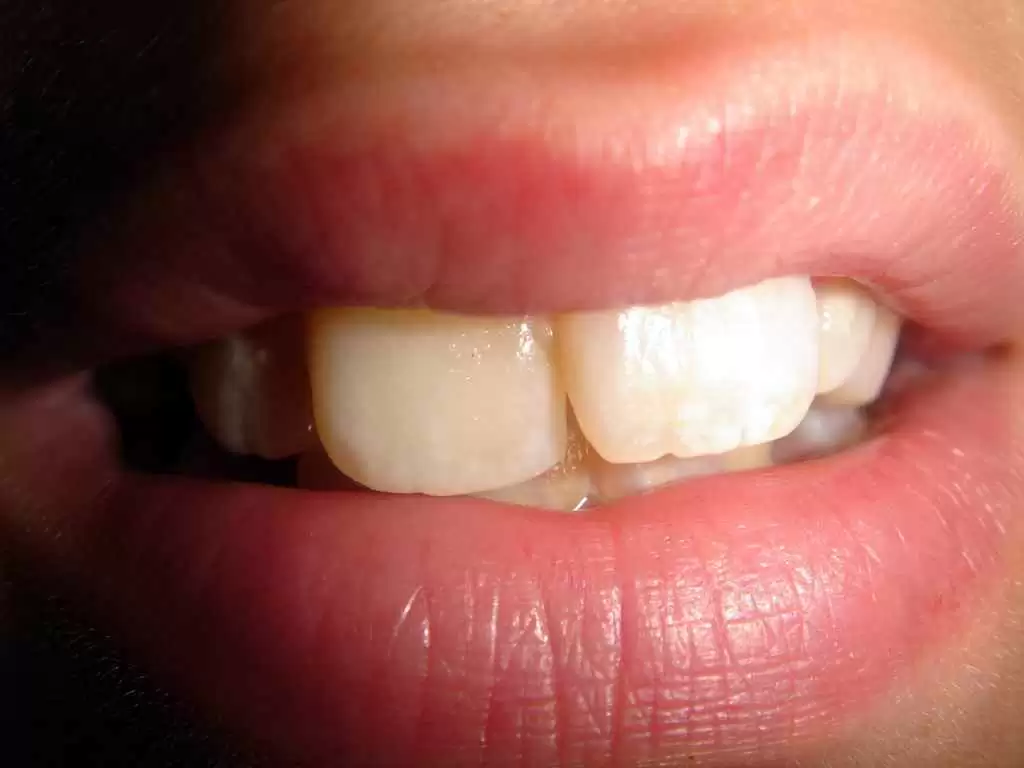
Enamel, composed of mineral crystals deposited on protein scaffolds, is essential for safeguarding teeth against damage. While defective enamel development can occur in about one out of every ten individuals, it is more prevalent in children with celiac disease. This condition can result in heightened sensitivity to temperature and acidic foods, as well as accelerated tooth decay.
The Discovery of a New Autoimmune Disorder
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
Prof. Abramson's study, published in Nature, has revealed a previously unknown autoimmune disorder affecting tooth enamel development. This disorder is prevalent in individuals with a rare genetic syndrome and children with celiac disease. By identifying this disorder, researchers aim to develop early detection methods and preventive strategies.
Understanding Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's cells or tissues. In the case of defective enamel development, the immune system targets proteins necessary for enamel formation. Mutations in the autoimmune regulator (Aire) gene, responsible for educating immune cells, can lead to impaired enamel production.
Implications for Celiac Disease
Individuals with celiac disease, a common autoimmune disorder, often exhibit enamel defects. Researchers have found autoantibodies attacking enamel proteins in both celiac patients and those with the newly discovered disorder. These antibodies, produced in response to food antigens like k-casein found in dairy products, may disrupt enamel development.
The Role of K-Casein
K-casein, a major component of dairy products, is implicated in enamel development. Antibodies against milk k-casein can potentially cross-react with human k-casein in teeth, leading to enamel flaws. Increased consumption of dairy products could elevate antibody levels, posing a risk to enamel health.
Implications for Early Diagnosis and Treatment
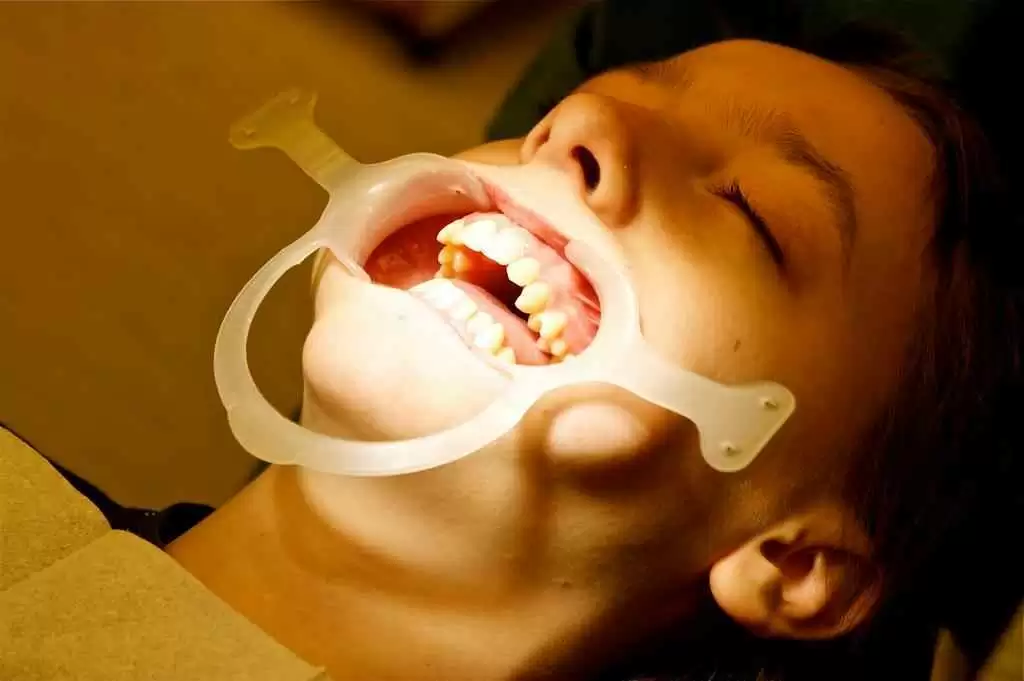
The identification of this new disorder and its association with enamel defects could pave the way for early diagnosis and preventive measures. Blood or saliva tests may enable early detection in children, allowing for timely intervention to preserve enamel health.
In conclusion, understanding the link between autoimmune disorders and defective enamel development provides valuable insights into oral health. By unraveling the underlying mechanisms, researchers aim to develop strategies for early detection and preventive treatment, benefiting individuals at risk of enamel defects.
Read more at: msn.com






Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now