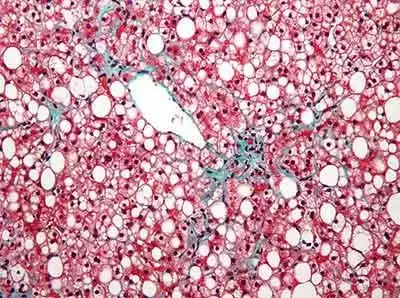
Celiac.com 08/12/2020 - The interaction between celiac disease and the liver is complex and not well understood. In some cases, isolated hypertransaminasemia is the only clear sign of celiac disease, while in other cases, liver diseases can occur with isolated tissue transglutaminase antibodies IgA (tTG IgA), but without the histologic markers that would indicate celiac disease.
A team of researchers recently set out to assess the results of tTG IgA testing for chronic liver disease (CLD) or cytolysis, and to seek out biopsy-confirmed celiac disease in patients with existing liver disease.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
The research team included Lena Cvetkovic, Gabriel Bernard, Nathanaelle Galette, Pierre-Olivier Hétu, Catherine Vincent, Mickael Bouin, and Amelie Therrien. They are variously affiliated with the Department of Medicine - Division of Gastroenterology, Centre de recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal, Montréal, Québec, Canada; the Department of Biochemistry, Centre de recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal, Montréal, Québec, Canada; and the Department of Medicine, Division of Hepatology, Centre de recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal in Montréal, Québec, Canada.
Their retrospective study used two groups. The first included 444 consecutive patients with no known celiac disease, for whom liver specialists had ordered tTG IgA testing. In this group, the team assessed the incidence of positive tTG and biopsy-confirmed celiac disease.
The second group included 212 consecutive individuals with positive tTG IgA and subsequent duodenal biopsies. In this group, the team assessed the frequency and clinical features of patients without biopsy-confirmed celiac disease, both with and without liver disease.
Tests conducted on the first patient group by a liver specialist turned up nine first time positive tTG IgA results. However, only six of these patients had biopsy-confirmed celiac disease. The second group included 33 individuals who also had liver disease, though nearly 43% showed no biopsy-confirmed celiac disease, compared with the 16% of patients who did not have liver disease.
Nearly two-thirds of the patients without biopsy-confirmed celiac disease showed an increase below three times the upper limit of normal of tTG IgA. Cases of chronic liver disease without elevated transaminase levels showed no association with celiac disease.
Testing liver disease patients for celiac disease can be helpful, but large numbers of patients may show positive celiac tests without any histological signs celiac disease.
Read more at J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug;3(4):185-193.






Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now