Celiac.com 03/03/2022 - When it comes to food allergy, there are basically two types:
Immediate Food Allergy (Classic, Immediate-Onset, IgE-Mediated)
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
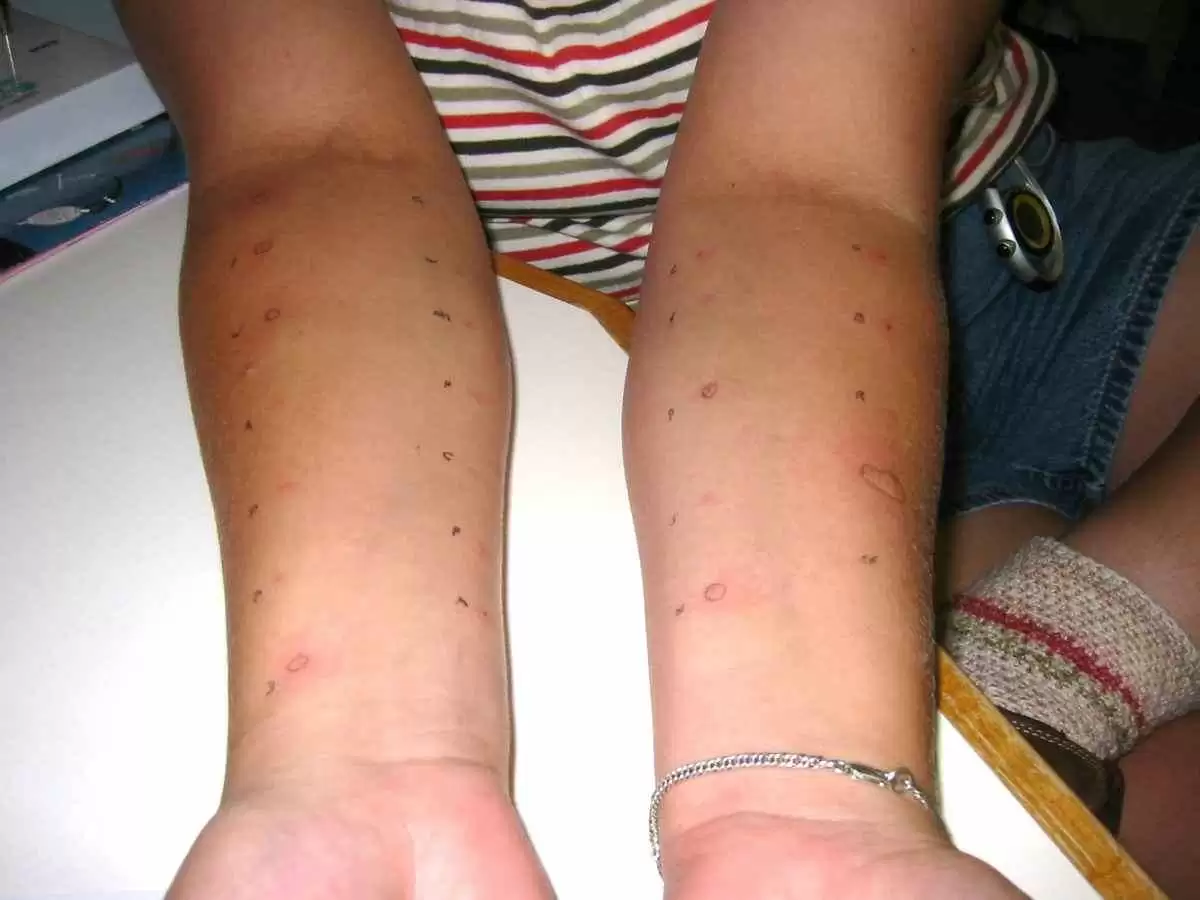
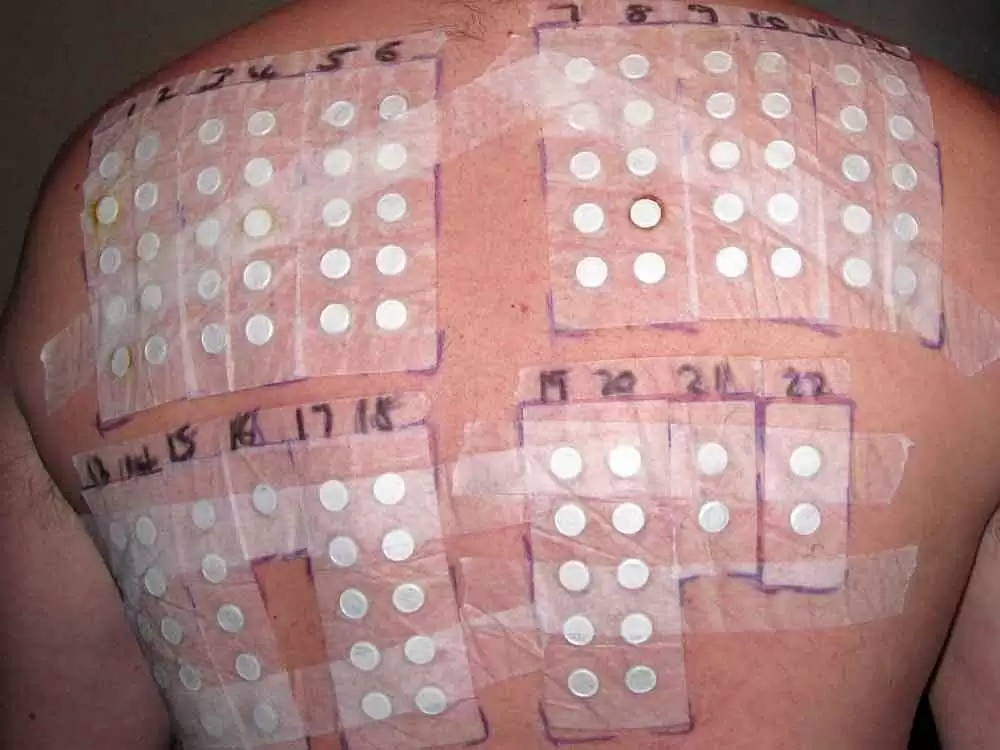
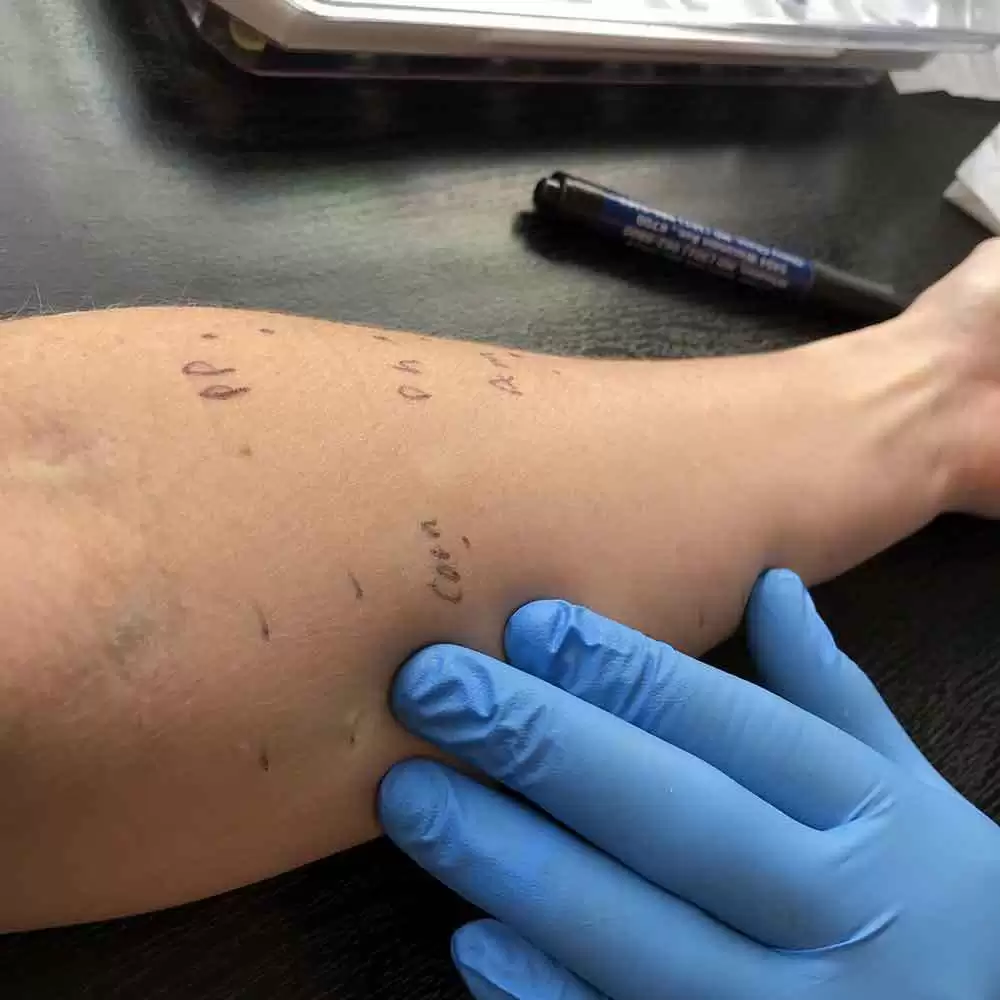
This is the most understood, but least-occurring immune response to foods. It only occurs in less than 2-3% of adults and less than 5% of children. The reaction time is anywhere from seconds to up to 2 hours and typically affects the skin, airways or the digestive system. The most commonly known response is anaphylaxis, which can result in death. This type of food allergy is typically tested in a doctor’s office by means of a skin “scratch” test. Additionally, it only takes a single food to cause such a reaction and it is typically a food that is rarely eaten.
Hidden Food Allergy (Food Intolerance, Delayed-Onset, IgG-Mediated)
This is the lesser understood, but most common immune response to foods. It occurs in anywhere from 45-60% of the general population and affects children and adults equally. The reaction time occurs anywhere from a couple of hours up to 2-3 days after consumption of the food. Any system, tissue and organ in the body can be affected, and there are over 118 medical conditions/symptoms that are either caused and/or provoked by this type of allergic response to foods including, but not limited to, arthritis, weight gain, fatigue, high blood pressure, arthritis, Celiac Disease, sinus conditions, asthma and various digestive disorders.
Conventional skin “scratch” testing is incapable of detecting this type of food allergy. Even more intriguing is that both a single food and a combination of foods can cause a reaction and it is usually with foods that are regularly eaten.
Conventional therapies for treating food allergy commonly include immune suppressing drugs such as steroids and anti-histamines, but there are a number of therapies that are less harmful to the body and in many cases are just as effective, which include:
-
Food Allergen Elimination and Rotation Diet: Though many adults can self-identify their or their children’s IgE-mediated (immediate-onset) allergic foods, it is not unusual for them to be unable to identify IgG-mediated (delayed-onset) allergic foods. Due to advancements in the laboratory analysis of food allergies in recent history, a simple and convenient finger-stick test is available for identifying the culprit foods behind one’s ill-health. This test can be done in either a physician’s office or in the comfort of one’s own home. Once the offending foods have been identified, a strict avoidance of allergic foods is the key to any food allergy treatment protocol. Eliminating the allergic foods will be the single most effective thing one can do to end the suffering they experience due to food-induced illnesses, and it will also help correct malnutrition and leaky gut syndrome.
The next most important thing one can do to treat their food allergy is to go on what is know as a rotation diet. A rotation diet helps prevent the development of new food allergies and encourages a more balanced, unprocessed and varied diet. It also leads to weight loss and helps eliminate food cravings that are caused by chemical mediators being released in the body by allergic reactions to foods. - Quercetin Bioflavanoid: Quercetin is a plant bioflavanoid that is naturally found in such things as apples, cherries, wine, tea, red and yellow onions, and chives. It has been found to help stabilize mast cells in allergic patients and is a very strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent.
- Glutamine: Glutamine is one of the most abundant amino acids in the body. It “feeds” the immune system and small intestinal mucosa and is critical for maintaining optimal levels of certain detoxifying antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase. When the body is stressed by food allergies and conditions such as Celiac Disease, Crohn’s Diseases and ulcerative colitis, glutamine is unable to do its job of maintaining a healthy immune system and intestinal lining. Glutamine increases the release of growth hormones, restores the digestive tract and maintains a healthy immune system. It also increases the liver’s and lymph nodes’ production of glutathione, which helps the body clear itself of food allergic antibody immune complexes. Glutamine also reverses low nutrient levels in food allergic patients suffering from malabsorption.
- MSM: Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is a natural component of the plants and animals we eat and is normally found in breast milk. MSM has been found to alleviate allergic responses to both foods and airborne inhalants such as pollen. It can provide relief to those who suffer from migraines and has been reported to offer long-term pain relief for those with rheumatoid arthritis. MSM aids in reversing constipation, acne, rosacea and snoring (all which have been associated with food allergy). There is a concern about contaminants in some MSM products. For instance, left over DMSO can cause an allergy in and of itself. Use only MSM products containing a distilled form, such as OptiMSM.
- Omega 3 Fatty Oils: Omega-3 oils, which can be found in fish such as salmon, halibut, haddock, flounder, cod, trout and red snapper, help in overriding the body’s ability to over-produce inflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which make the body more prone to allergies and inflammation.
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A is an important immune system building vitamin. It helps prevent skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. It aids in maintaining a healthy thymus gland and helps prevent the release of inflammatory prostaglandin during allergic reactions.
- Vitamin C - Vitamin C has long been regarded as a natural antihistamine. It also stimulates phagocytes, which is a white blood cell that attacks food allergens and various viruses and bacteria.
- Breast Feeding: Breastfeeding improves promotes healthy probiotic bacteria in the intestines and passes protective antibodies and nutrients from the mother to the infant, which protects against allergies and other ill-health conditions. Those who are breast-fed have been shown to have a lower incidence of otitis media, eczema, asthma, diarrhea and insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Exercise: Exercise improves circulation, enhances digestion, stimulates the immune system, and accelerates detoxification—all which aid in reversing and preventing food allergy.
- Elimination: Eliminating some of the initial causes a food allergy is always important for both treatment and prevention. People tend to develop delayed onset food allergies during antibiotic treatment or when taking anti-inflammatory drugs or acid blocking drugs for prolonged periods of time.






Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now