Celiac.com 09/12/2024 - Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This condition affects roughly one in 133 people worldwide, though it often goes undiagnosed due to its diverse symptoms. Celiac disease can co-occur with other autoimmune diseases, complicating its presentation and management. The disease’s prevalence and diagnosis are influenced by demographic and genetic factors, making it a significant health concern globally.
Ophthalmic Manifestations of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is not just a gastrointestinal disorder; it can also have various ophthalmic manifestations. Patients with celiac disease may exhibit a range of eye-related issues that are not typically associated with the condition, such as decreased endothelial cell density, vitamin A deficiency causing dryness, altered corneal nerve density, cataracts, uveitis, changes in choroidal thickness, papilledema, and neurological issues like nystagmus. These manifestations highlight the systemic nature of celiac disease and the importance of comprehensive care.
The Need for Thorough Evaluation Before Corneal Refractive Surgery
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
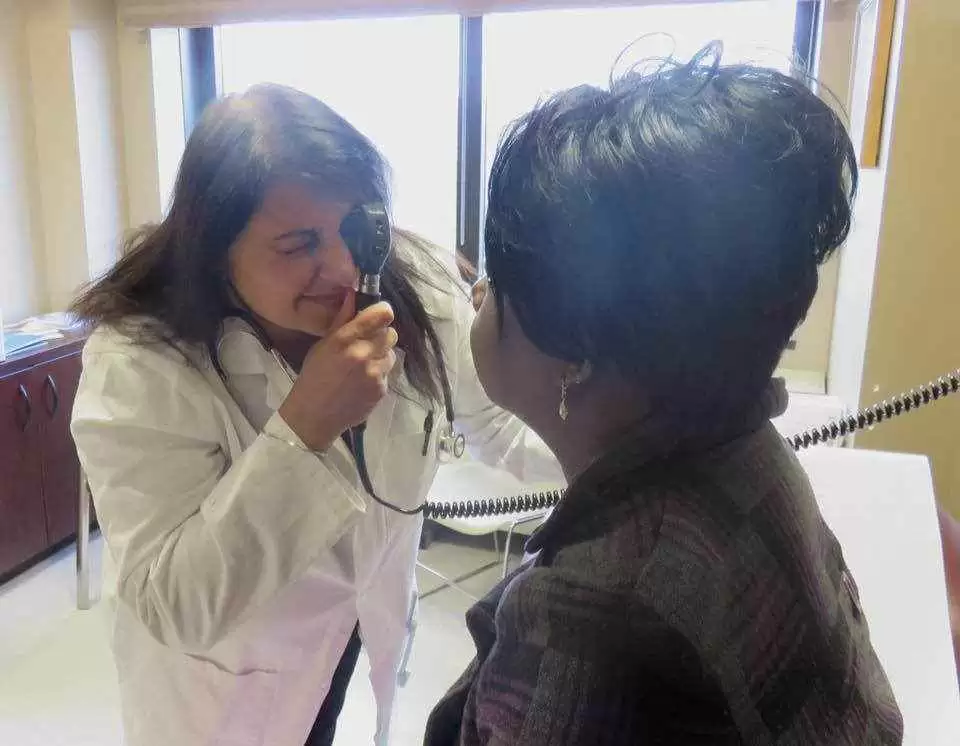
Corneal refractive surgery, which includes procedures like LASIK, is increasingly popular for correcting vision problems. However, for patients with celiac disease, it is crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation before proceeding with such surgeries. The variability in ocular manifestations among celiac patients necessitates individualized assessments to determine surgical candidacy and optimize outcomes. This evaluation should include both subjective and objective assessments.
Subjective Assessments
A detailed medical history focusing on the patient’s experience with celiac disease is essential. This includes questions about dietary gluten intake, weight loss, joint pain, and cognitive impairments like brain fog. Understanding these aspects can help in identifying potential complications that might affect surgical outcomes.
Objective Assessments
A comprehensive objective assessment should include several diagnostic tests:
- Slit-lamp biomicroscopy to examine the eye’s structures.
- Schirmer test and tear break-up time (TBUT) to assess tear production and dry eye.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) to measure retinal and choroidal thickness.
- Scheimpflug imaging and fundoscopy to evaluate the anterior and posterior segments of the eye.
Specific Considerations for Celiac Disease Patients
Given the diverse ocular manifestations associated with celiac disease, several specific considerations should be addressed:
- Dry Eye Disease: Patients with celiac disease are more prone to dry eye disease. Symptoms like ocular discomfort, irritation, redness, and burning can be managed with artificial tears and punctal plugs before surgery.
- Endothelial Cell Density (ECD): Celiac disease patients may have lower ECD, which can lead to corneal edema post-surgery. Specular microscopy is recommended to evaluate ECD before proceeding with surgery.
- Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD): Some celiac disease patients might have shallower ACDs, which can indicate early-onset cataracts. Scheimpflug imaging can help assess ACD.
- Choroidal and Retinal Health: OCT is crucial to evaluate choroidal thickness and retinal health. Thinner choroids and other posterior segment abnormalities can affect visual outcomes post-surgery.
- Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy (TAO): Celiac disease patients may also suffer from TAO, which can impact corneal health and refractive surgery outcomes. Thyroid function tests and orbital ultrasound are necessary for a thorough evaluation.
- Vitamin A Deficiency: This can lead to dryness and other ocular surface issues. Serum retinol levels should be checked, and vitamin A supplementation should be managed appropriately.
- Neurological Issues: Conditions like gluten ataxia and nystagmus can complicate surgery due to motor control issues. These conditions need careful assessment and management.
- Autoimmune Co-morbidities: The presence of other autoimmune conditions, like Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, can increase the risk of complications like diabetic retinopathy, impacting surgical outcomes. Comprehensive retinal evaluations are necessary in these cases.
Conclusion: The Importance of Comprehensive Care
This study underscores the need for a thorough and individualized evaluation of celiac disease patients considering corneal refractive surgery. By addressing the various ophthalmic manifestations and related autoimmune conditions, healthcare providers can improve surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction. The recommendations provided in this study serve as preliminary guidelines, highlighting the importance of further research to better understand the impact of celiac disease on corneal refractive surgery outcomes. For celiac patients, these insights are crucial, as they emphasize the need for comprehensive care and tailored management strategies to ensure the best possible surgical results.
Read more at: cureus.com









Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now