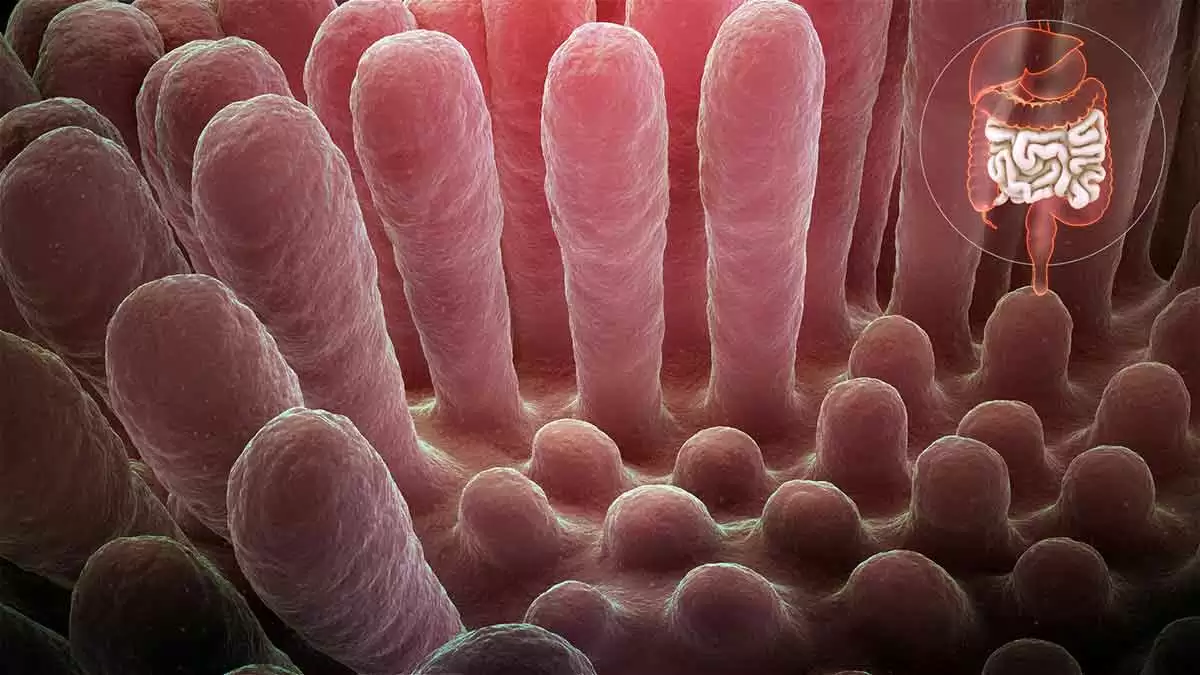
Celiac.com 06/01/2021 - Villous atrophy not caused by celiac disease is called "non-celiac enteropathy." In many cases, the symptoms mirror the classic symptoms of celiac disease: diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Spotting the difference between celiac disease and non-celiac enteropathy can be challenging. That's why physicians recommend celiac disease blood tests, which are used to find adverse immune reactions to the gluten protein in the foods you eat.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
Just as it's possible to have damaged villi without celiac disease, it's possible to have celiac disease, and villi damage, even with negative blood antibody tests.
People with celiac disease usually improve on a gluten-free diet. While some may not, many folks with non-celiac enteropathy do not respond to a gluten-free diet.
People who do not see symptom improvement on a gluten-free diet may need to consider alternative causes for their symptoms and villous atrophy.
Non-Celiac Causes of Villous Atrophy
Non-celiac causes of villous atrophy include:
Benicar (olmesartan)
In some patients, taking this blood pressure medication leads to villous atrophy combined with diarrhea and weight loss. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued a warning about this in 2013.
Common Variable Immune Deficiency, or CVID
CVID is a condition that leaves people vulnerable to recurrent infections.
Crohn's disease
Villous atrophy is unusual in Crohn's disease, but can happen.
Lymphoma
One study found two different types of lymphoma could cause villous atrophy: small intestinal T-cell lymphoma, and enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma. Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma is closely linked to celiac disease.
Casein/Cow's Milk Intolerance
Research has shown that flattened villi can also be caused by casein intolerance. For more info see "Mucosal reactivity to cow's milk protein in C(o)eliac disease," which states "A mucosal inflammatory response similar to that elicited by gluten was produced by CM (Cows Milk) protein in about 50% of the patients with coeliac disease. Casein, in particular, seems to be involved in this reaction."
Certain Drugs
Drugs that suppress your immune system (such as Imuran and CellCept), the antibiotic neomycin, and the anti-inflammatory medication Colcrys, also have been linked to reports of medication-induced villous atrophy.
Small intestine Bacterial Overgrowth, or SIBO
Symptoms of SIBO can mimic those of celiac disease.
Other possible causes of villous atrophy, including infection with parasites or with the ulcer-causing bacteria Helicobacter pylori, also have been reported.
Thiamine Deficiency and/or Beri Beri
Both can cause thinning of the villi, leading to both casein/lactose intolerance and in time possibly a celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) diagnosis.
Not all Villous Atrophy is From Celiac Disease
Most, but not all, cases of villous atrophy are caused by celiac disease. Patients with negative blood test, who do not see symptoms improve on a gluten-free diet, should consult with a doctor about other possible causes of villous atrophy.









Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now