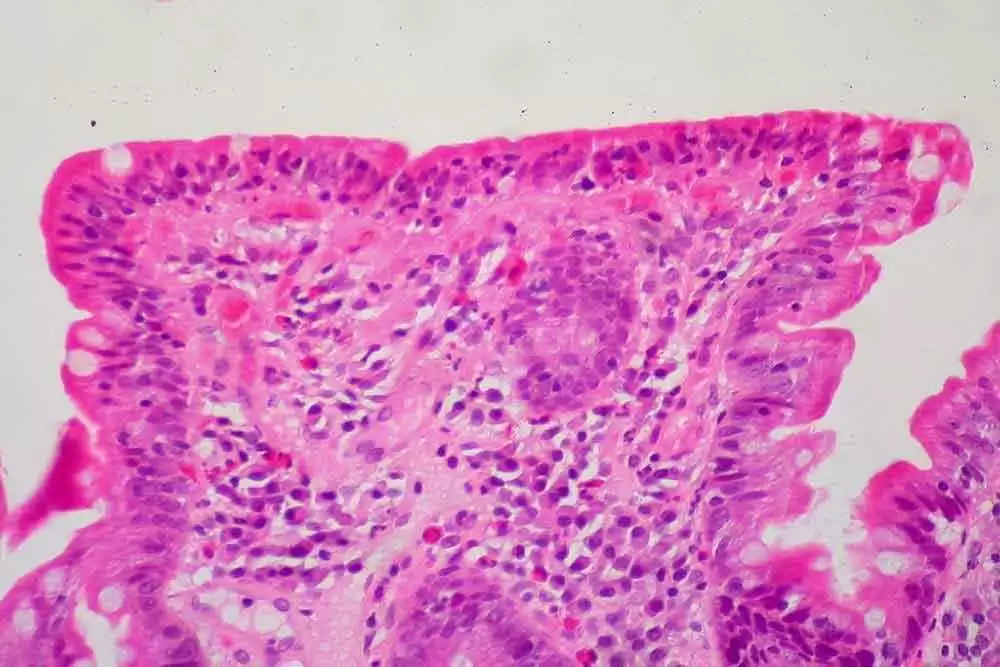
WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that affects around 1.4% of the population (91.2 million people worldwide, and 3.9 million in the U.S.A.). People with celiac disease suffer an autoimmune reaction when they consume wheat, rye or barley. The immune reaction is triggered by certain proteins in the wheat, rye, or barley, and, left untreated, causes damage to the small, finger-like structures, called villi, that line the gut. The damage occurs as shortening and villous flattening in the lamina propria and crypt regions of the intestines. The damage to these villi then leads to numerous other issues that commonly plague people with untreated celiac disease, including poor nutritional uptake, fatigue, and myriad other problems.
Celiac disease mostly affects people of Northern European descent, but recent studies show that it also affects large numbers of people in Italy, China, Iran, India, and numerous other places thought to have few or no cases.
Celiac.com Sponsor (A12):
Celiac disease is most often uncovered because people experience symptoms that lead them to get tests for antibodies to gluten. If these tests are positive, then the people usually get biopsy confirmation of their celiac disease. Once they adopt a gluten-free diet, they usually see gut healing, and major improvements in their symptoms.
CLASSIC CELIAC DISEASE SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of celiac disease can range from the classic features, such as diarrhea, upset stomach, bloating, gas, weight loss, and malnutrition, among others.
LESS OBVIOUS SYMPTOMS
Celiac disease can often less obvious symptoms, such fatigue, vitamin and nutrient deficiencies, anemia, to name a few. Often, these symptoms are regarded as less obvious because they are not gastrointestinal in nature. You got that right, it is not uncommon for people with celiac disease to have few or no gastrointestinal symptoms. That makes spotting and connecting these seemingly unrelated and unclear celiac symptoms so important.
NO SYMPTOMS
Currently, most people diagnosed with celiac disease do not show symptoms, but are diagnosed on the basis of referral for elevated risk factors.
CELIAC DISEASE VS. GLUTEN INTOLERANCE
Gluten intolerance is a generic term for people who have some sort of sensitivity to gluten. These people may or may not have celiac disease. Researchers generally agree that there is a condition called non-celiac gluten sensitivity. That term has largely replaced the term gluten-intolerance. What’s the difference between celiac disease and non-celiac gluten-sensitivity?
CELIAC DISEASE VS. NON-CELIAC GLUTEN SENSITIVITY (NCGS)
Gluten triggers symptoms and immune reactions in people with celiac disease. Gluten can also trigger symptoms in some people with NCGS, but the similarities largely end there.
There are four main differences between celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity:
-
No Hereditary Link in NCGS
Researchers know for certain that genetic heredity plays a major role in celiac disease. If a first-degree relative has celiac disease, then you have a statistically higher risk of carrying genetic markers DQ2 and/or DQ8, and of developing celiac disease yourself. NCGS is not known to be hereditary. Some research has shown certain genetic associations, such as some NCGS patients, but there is no proof that NCGS is hereditary. -
No Connection with Celiac-related Disorders
Unlike celiac disease, NCGS is so far not associated with malabsorption, nutritional deficiencies, or a higher risk of autoimmune disorders or intestinal malignancies. -
No Immunological or Serological Markers
People with celiac disease nearly always test positive for antibodies to gluten proteins. Researchers have, as yet, identified no such antobodies or serologic markers for NCGS. That means that, unlike with celiac disease, there are no telltale screening tests that can point to NCGS. -
Absence of Celiac Disease or Wheat Allergy
Doctors diagnose NCGS only by excluding both celiac disease, an IgE-mediated allergy to wheat, and by the noting ongoing adverse symptoms associated with gluten consumption.
WHAT ABOUT IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME (IBS) AND IRRITABLE BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)?
IBS and IBD are usually diagnosed in part by ruling out celiac disease. Many patients with irritable bowel syndrome are sensitive to gluten. Many experience celiac disease-like symptoms in reaction to wheat. However, patients with IBS generally show no gut damage, and do not test positive for antibodies to gliadin and other proteins as do people with celiac disease. Some IBS patients also suffer from NCGS.
To add more confusion, many cases of IBS are, in fact, celiac disease in disguise.
That said, people with IBS generally react to more than just wheat. People with NCGS generally react to wheat and not to other things, but that’s not always the case. Doctors generally try to rule out celiac disease before making a diagnosis of IBS or NCGS.
Crohn’s Disease and celiac disease share many common symptoms, though causes are different. In Crohn’s disease, the immune system can cause disruption anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, and a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease typically requires more diagnostic testing than does a celiac diagnosis.
Crohn’s treatment consists of changes to diet and possible surgery. Up to 10% of Crohn's patients can have both of conditions, which suggests a genetic connection, and researchers continue to examine that connection.
- Is There a Connection Between Celiac Disease, Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity and Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
- Large Number of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients Sensitive To Gluten
- Some IBD Patients also Suffer from Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
- Many Cases of IBS and Fibromyalgia Actually Celiac Disease in Disguise
CELIAC DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of celiac disease can be difficult.
Perhaps because celiac disease presents clinically in such a variety of ways, proper diagnosis often takes years. A positive serological test for antibodies against tissue transglutaminase is considered a very strong diagnostic indicator, and a duodenal biopsy revealing villous atrophy is still considered by many to be the diagnostic gold standard.
But this idea is being questioned; some think the biopsy is unnecessary in the face of clear serological tests and obvious symptoms. Also, researchers are developing accurate and reliable ways to test for celiac disease even when patients are already avoiding wheat. In the past, patients needed to be consuming wheat to get an accurate test result.
- Celiac disease can have numerous vague, or confusing symptoms that can make diagnosis difficult.
- Celiac disease is commonly misdiagnosed by doctors.
- Read a Personal Story About Celiac Disease Diagnosis from the Founder of Celiac.com
Currently, testing and biopsy still form the cornerstone of celiac diagnosis.
TESTING
There are several serologic (blood) tests available that screen for celiac disease antibodies, but the most commonly used is called a tTG-IgA test. If blood test results suggest celiac disease, your physician will recommend a biopsy of your small intestine to confirm the diagnosis.
Testing is fairly simple and involves screening the patients blood for antigliadin (AGA) and endomysium antibodies (EmA), and/or doing a biopsy on the areas of the intestines mentioned above, which is still the standard for a formal diagnosis. Also, it is now possible to test people for celiac disease without making them concume wheat products.
BIOPSY
Until recently, biopsy confirmation of a positive gluten antibody test was the gold standard for celiac diagnosis. It still is, but things are changing fairly quickly. Children can now be accurately diagnosed for celiac disease without biopsy. Diagnosis based on level of TGA-IgA 10-fold or more the ULN, a positive result from the EMA tests in a second blood sample, and the presence of at least 1 symptom could avoid risks and costs of endoscopy for more than half the children with celiac disease worldwide.
WHY A GLUTEN-FREE DIET?
Currently the only effective, medically approved treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet. Following a gluten-free diet relieves symptoms, promotes gut healing, and prevents nearly all celiac-related complications.
A gluten-free diet means avoiding all products that contain wheat, rye and barley, or any of their derivatives. This is a difficult task as there are many hidden sources of gluten found in the ingredients of many processed foods. Still, with effort, most people with celiac disease manage to make the transition. The vast majority of celiac disease patients who follow a gluten-free diet see symptom relief and experience gut healing within two years.
For these reasons, a gluten-free diet remains the only effective, medically proven treatment for celiac disease.
WHAT ABOUT ENZYMES, VACCINES, ETC.?
There is currently no enzyme or vaccine that can replace a gluten-free diet for people with celiac disease.
There are enzyme supplements currently available, such as AN-PEP, Latiglutetenase, GluteGuard, and KumaMax, which may help to mitigate accidental gluten ingestion by celiacs. KumaMax, has been shown to survive the stomach, and to break down gluten in the small intestine. Latiglutenase, formerly known as ALV003, is an enzyme therapy designed to be taken with meals. GluteGuard has been shown to significantly protect celiac patients from the serious symptoms they would normally experience after gluten ingestion. There are other enzymes, including those based on papaya enzymes.
Additionally, there are many celiac disease drugs, enzymes, and therapies in various stages of development by pharmaceutical companies, including at least one vaccine that has received financial backing. At some point in the not too distant future there will likely be new treatments available for those who seek an alternative to a lifelong gluten-free diet.
For now though, there are no products on the market that can take the place of a gluten-free diet. Any enzyme or other treatment for celiac disease is intended to be used in conjunction with a gluten-free diet, not as a replacement.
ASSOCIATED DISEASES
The most common disorders associated with celiac disease are thyroid disease and Type 1 Diabetes, however, celiac disease is associated with many other conditions, including but not limited to the following autoimmune conditions:
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: 2.4-16.4%
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): 11%
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: 4-6%
- Autoimmune hepatitis: 6-15%
- Addison disease: 6%
- Arthritis: 1.5-7.5%
- Sjögren’s syndrome: 2-15%
- Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: 5.7%
- IgA Nephropathy (Berger’s Disease): 3.6%
Other celiac co-morditities include:
- Crohn’s Disease; Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Chronic Pancreatitis
- Down Syndrome
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Lupus
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Scleroderma
- Turner Syndrome
- Ulcerative Colitis; Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Williams Syndrome
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (intestinal and extra-intestinal, T- and B-cell types)
- Small intestinal adenocarcinoma
- Esophageal carcinoma
- Papillary thyroid cancer
- Melanoma
CELIAC DISEASE REFERENCES:
- Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2018;16:823–836
- Celiac Disease Center, Columbia University
- Gluten Intolerance Group
- National Institutes of Health
- U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Mayo Clinic
- University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center







Recommended Comments
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now