-
Welcome to Celiac.com!
You have found your celiac tribe! Join us and ask questions in our forum, share your story, and connect with others.
-
Celiac.com Sponsor (A1):
Celiac.com Sponsor (A1-M):
-
Get Celiac.com Updates:Support Our Content
Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'vitamin a'.
-
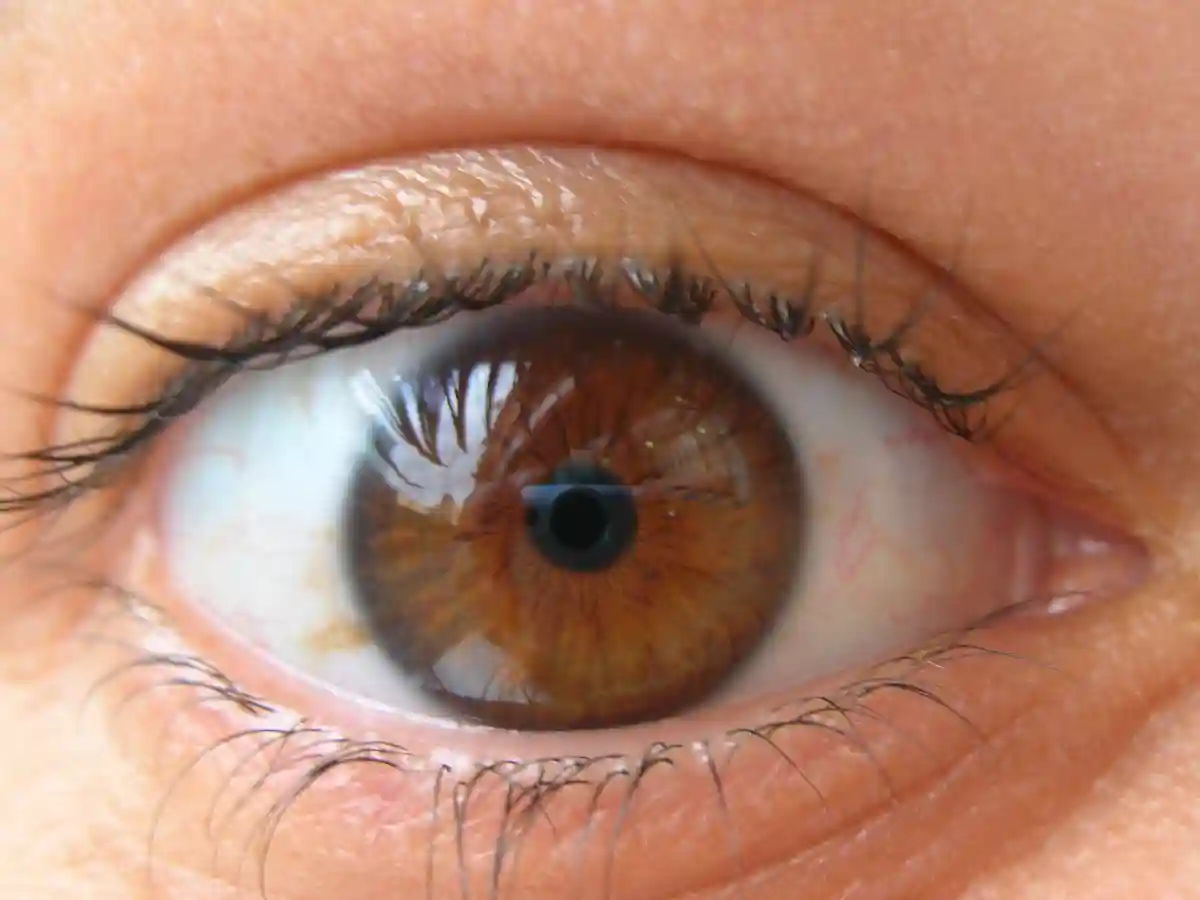
Celiac.com 09/12/2024 - Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This condition affects roughly one in 133 people worldwide, though it often goes undiagnosed due to its diverse symptoms. Celiac disease can co-occur with other autoimmune diseases, complicating its presentation and management. The disease’s prevalence and diagnosis are influenced by demographic and genetic factors, making it a significant health concern globally. Ophthalmic Manifestations of Celiac Disease Celiac disease is not just a gastrointestinal disorder; it can also have various ophthalmic manifestations. Patients with celiac disease may exhibit a range of eye-related issues that are not typically associated with the condition, such as decreased endothelial cell density, vitamin A deficiency causing dryness, altered corneal nerve density, cataracts, uveitis, changes in choroidal thickness, papilledema, and neurological issues like nystagmus. These manifestations highlight the systemic nature of celiac disease and the importance of comprehensive care. The Need for Thorough Evaluation Before Corneal Refractive Surgery Corneal refractive surgery, which includes procedures like LASIK, is increasingly popular for correcting vision problems. However, for patients with celiac disease, it is crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation before proceeding with such surgeries. The variability in ocular manifestations among celiac patients necessitates individualized assessments to determine surgical candidacy and optimize outcomes. This evaluation should include both subjective and objective assessments. Subjective Assessments A detailed medical history focusing on the patient’s experience with celiac disease is essential. This includes questions about dietary gluten intake, weight loss, joint pain, and cognitive impairments like brain fog. Understanding these aspects can help in identifying potential complications that might affect surgical outcomes. Objective Assessments A comprehensive objective assessment should include several diagnostic tests: Slit-lamp biomicroscopy to examine the eye’s structures. Schirmer test and tear break-up time (TBUT) to assess tear production and dry eye. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) to measure retinal and choroidal thickness. Scheimpflug imaging and fundoscopy to evaluate the anterior and posterior segments of the eye. Specific Considerations for Celiac Disease Patients Given the diverse ocular manifestations associated with celiac disease, several specific considerations should be addressed: Dry Eye Disease: Patients with celiac disease are more prone to dry eye disease. Symptoms like ocular discomfort, irritation, redness, and burning can be managed with artificial tears and punctal plugs before surgery. Endothelial Cell Density (ECD): Celiac disease patients may have lower ECD, which can lead to corneal edema post-surgery. Specular microscopy is recommended to evaluate ECD before proceeding with surgery. Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD): Some celiac disease patients might have shallower ACDs, which can indicate early-onset cataracts. Scheimpflug imaging can help assess ACD. Choroidal and Retinal Health: OCT is crucial to evaluate choroidal thickness and retinal health. Thinner choroids and other posterior segment abnormalities can affect visual outcomes post-surgery. Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy (TAO): Celiac disease patients may also suffer from TAO, which can impact corneal health and refractive surgery outcomes. Thyroid function tests and orbital ultrasound are necessary for a thorough evaluation. Vitamin A Deficiency: This can lead to dryness and other ocular surface issues. Serum retinol levels should be checked, and vitamin A supplementation should be managed appropriately. Neurological Issues: Conditions like gluten ataxia and nystagmus can complicate surgery due to motor control issues. These conditions need careful assessment and management. Autoimmune Co-morbidities: The presence of other autoimmune conditions, like Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, can increase the risk of complications like diabetic retinopathy, impacting surgical outcomes. Comprehensive retinal evaluations are necessary in these cases. Conclusion: The Importance of Comprehensive Care This study underscores the need for a thorough and individualized evaluation of celiac disease patients considering corneal refractive surgery. By addressing the various ophthalmic manifestations and related autoimmune conditions, healthcare providers can improve surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction. The recommendations provided in this study serve as preliminary guidelines, highlighting the importance of further research to better understand the impact of celiac disease on corneal refractive surgery outcomes. For celiac patients, these insights are crucial, as they emphasize the need for comprehensive care and tailored management strategies to ensure the best possible surgical results. Read more at: cureus.com
- 1 comment
-
- celiac disease
- corneal erosion
- (and 7 more)
-
Celiac.com 07/29/2020 - Vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies are common in people with both treated and untreated celiac disease. Fortifying processed foods with vitamins and micronutrients is common method for enhancing public health. In the latest iteration of that practice, researchers Dr David Aldridge and PhD student David Willer, from Cambridge University and UK company BioBullets, have figured out a way to deliver fortified levels of vitamins in bivalve shellfish such as oysters, clams and mussels by using new micro-encapsulation technology. The resulting shellfish offer a way to get high levels of vitamins into people with vitamin deficiencies. The results offer promise for people with chronic vitamin deficiencies, including those with celiac and other diseases. The team is now working with major seafood manufacturers to further test and optimize the efficacy of their "Bio Bullets" micro-encapsulation process. Shellfish fed Vitamin A and D fortified microcapsules for eight hours while being held in cleansing tanks after harvest, showed the most promise. Aldrige and Willer found that fortified oysters provide about 100 times more Vitamin A, and over 150 times more Vitamin D, than natural oysters, and far more than Salmon, a good natural source for these nutrients. In fact, a serving of just two supercharged shellfish a day met the U.S. recommended daily allowance for both vitamins A and D. The shellfish are also environmentally friendly, and highly sustainable, with a lower energy demand than animal meat, fish, or many plant crops such as wheat, soya, and rice. Fortifying shellfish with vitamins offers a "cheap and effective way to get micronutrients into a sustainable and delicious source of protein. Targeted use of this technology in regions worst affected by nutrient deficiencies...could help improve the health of millions," says Willer. Obviously, some people cannot eat shellfish, but the vast majority of people can, including people with celiac disease. For people with celiac disease who face challenges with vitamin and micronutrient deficiency, fortified shellfish could offer a tasty, easy way to load up on essential vitamins, which will likely improve overall health and wellbeing. This technology could be a gamer changer for both celiacs, and for other people across the globe who are suffering from vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies. Read more in Newfoodmagazine.com
-
- deficiency
- fortified
- (and 7 more)
-
Celiac.com 07/17/2018 - What can fat soluble vitamin levels in newly diagnosed children tell us about celiac disease? A team of researchers recently assessed fat soluble vitamin levels in children diagnosed with newly celiac disease to determine whether vitamin levels needed to be assessed routinely in these patients during diagnosis. The researchers evaluated the symptoms of celiac patients in a newly diagnosed pediatric group and evaluated their fat soluble vitamin levels and intestinal biopsies, and then compared their vitamin levels with those of a healthy control group. The research team included Yavuz Tokgöz, Semiha Terlemez and Aslıhan Karul. They are variously affiliated with the Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, the Department of Pediatrics, and the Department of Biochemistry at Adnan Menderes University Medical Faculty in Aydın, Turkey. The team evaluated 27 female, 25 male celiac patients, and an evenly divided group of 50 healthy control subjects. Patients averaged 9 years, and weighed 16.2 kg. The most common symptom in celiac patients was growth retardation, which was seen in 61.5%, with abdominal pain next at 51.9%, and diarrhea, seen in 11.5%. Histological examination showed nearly half of the patients at grade Marsh 3B. Vitamin A and vitamin D levels for celiac patients were significantly lower than the control group. Vitamin A and vitamin D deficiencies were significantly more common compared to healthy subjects. Nearly all of the celiac patients showed vitamin D insufficiency, while nearly 62% showed vitamin D deficiency. Nearly 33% of celiac patients showed vitamin A deficiency. The team saw no deficiencies in vitamin E or vitamin K1 among celiac patients. In the healthy control group, vitamin D deficiency was seen in 2 (4%) patients, vitamin D insufficiency was determined in 9 (18%) patients. The team found normal levels of all other vitamins in the healthy group. Children with newly diagnosed celiac disease showed significantly reduced levels of vitamin D and A. The team recommends screening of vitamin A and D levels during diagnosis of these patients. Source: BMC Pediatrics
- 2 comments
-
- celiac
- celiac disease
-
(and 6 more)
Tagged with:
Celiac.com Sponsor (A8):
Celiac.com Sponsor (A8):
Celiac.com Sponsor (A8-M):